H C Verma Solutions for Chapter: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter, Exercise 3: OBJECTIVE II
H C Verma Physics Solutions for Exercise - H C Verma Solutions for Chapter: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter, Exercise 3: OBJECTIVE II
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 14: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter, Exercise 3: OBJECTIVE II with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. CONCEPTS OF PHYSICS [VOLUME 1] solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from H C Verma Solutions for Chapter: Some Mechanical Properties of Matter, Exercise 3: OBJECTIVE II with Hints & Solutions
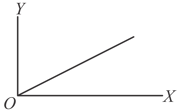
A student plots a graph from his readings on the determination of Young's modulus of a metal wire but forgets to put the labels. The quantities on the - and -axes may be, respectively,
The properties of a surface are different from those of the bulk liquid because the surface molecules
The rise of a liquid in a capillary tube depends on
The contact angle between a solid and a liquid is a property of
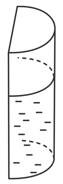
A liquid is contained in a vertical tube of a semicircular cross-section. The contact angle is zero. The force of surface tension on the curved part and the flat part is in the ratio
When a capillary tube is dipped into a liquid, the liquid neither rises nor falls in the capillary.
A solid sphere moves at a terminal velocity of in the air at a place where . The sphere is taken in a gravity-free hall having air at the same pressure and pushed down at a speed of .
